今天补发一个六月份给朋友做的一个vue+百度地图的微教程,这个教程本来是做在我的有道云笔记上的,今天特意去我有道云上搜出来这篇教程,让大家能够更轻松的写出地图相关功能!
此教程我主要教vue-baidu-map这个插件的使用,然后会补充一下百度地图原生api的用法
地图相关介绍:
生活中哪里会用到地图
最常见的:手机导航、车载导航、外卖app、同城跑腿配送类app、微信定位
地图api两大平台
国内常用百度地图api和高德地图api
百度地图开放平台:https://lbsyun.baidu.com/
高德地图开放平台:https://lbs.amap.com/
百度地图api接口文档
注意:接口文档有很多对应的类型,如果从官网进去找接口,我们需要选择支持javascript代码的文档
百度api秘钥获取
所有需要定位功能的代码,最终都会用到地图api,用地图api就需要注册,然后去申请,填写对应的内容即可申请到api秘钥【秘钥类似于调用百度api接口的身份证】
vue-baidu-map组件:
vue-baidu-map是什么
组件安装
npm命令:
npm install vue-baidu-map --save
CDN方式(src引入):
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-baidu-map"></script>
全局注册
/* vue-baidu-map注册 */
import BaiduMap from 'vue-baidu-map'
Vue.use(BaiduMap, {
ak: 'd8zxnvqFie4boLsuUtRD1TB38oskalKL'
})
小demo实现:
1、创建demo
将组件放入页面即可
<baidu-map class="bm-view" center="北京" ak="d8zxnvqFie4boLsuUtRD1TB38oskalKL" />
2、方法和属性
center:组件的默认值
zoom:地图默认比例
ready:组件展开后执行的默认异步函数(执行一次)
lng:经度
lat:纬度
<template>
<div id="app">
<baidu-map class="bm-view" :center="center" :zoom="zoom" @ready="handler" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {
center: { lng: 0, lat: 0 },
zoom: 3
}
},
methods: {
handler({ BMap, map }) {
console.log(BMap, map)
this.center.lng = 116.404
this.center.lat = 39.915
this.zoom = 15
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.bm-view {
width: 100%;
height: 600px;
}
</style>电子围栏手动绘制:
<template>
<div id="app">
<baidu-map class="bm-view" center="北京" :zoom="zoom" @mousemove="syncPolyline"
@click="paintPolyline"
@rightclick="newPolyline">
<bm-control>
<button @click="toggle('polyline')">{{ polyline.editing ? '停止绘制' : '开始绘制' }}</button>
</bm-control>
<bm-polyline :path="path" v-for="path of polyline.paths" :key="path"></bm-polyline>
</baidu-map>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {
center: { lng: 0, lat: 0 },
zoom: 3,
polyline: {
editing: false,
paths: []
}
}
},
methods: {
handler({ BMap, map }) {
console.log(BMap, map)
this.center.lng = 116.404
this.center.lat = 39.915
this.zoom = 15
},
//
toggle (name) {
this[name].editing = !this[name].editing
},
syncPolyline (e) {
if (!this.polyline.editing) {
return
}
const {paths} = this.polyline
if (!paths.length) {
return
}
const path = paths[paths.length - 1]
if (!path.length) {
return
}
if (path.length === 1) {
path.push(e.point)
}
this.$set(path, path.length - 1, e.point)
},
newPolyline (e) {
if (!this.polyline.editing) {
return
}
const {paths} = this.polyline
if(!paths.length) {
paths.push([])
}
const path = paths[paths.length - 1]
path.pop()
if (path.length) {
paths.push([])
}
},
paintPolyline (e) {
if (!this.polyline.editing) {
return
}
const {paths} = this.polyline
!paths.length && paths.push([])
paths[paths.length - 1].push(e.point)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.bm-view {
width: 100%;
height: 600px;
}
</style>电子围栏绘制:
<template>
<baidu-map class="bm-view" :center="{lng: 116.404, lat: 39.915}" :zoom="15">
<bm-polygon :path="polygonPath" stroke-color="blue" :stroke-opacity="0.5" :stroke-weight="2" :editing="true" @lineupdate="updatePolygonPath"/>
</baidu-map>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
polygonPath: [
{lng: 116.412732, lat: 39.911707},
{lng: 116.39455, lat: 39.910932},
{lng: 116.403461, lat: 39.921336}
]
}
},
methods: {
updatePolygonPath (e) {
this.polygonPath = e.target.getPath()
},
addPolygonPoint () {
this.polygonPath.push({lng: 116.404, lat: 39.915})
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.bm-view {
width: 100%;
height: 600px;
}
</style>百度地图原生api:
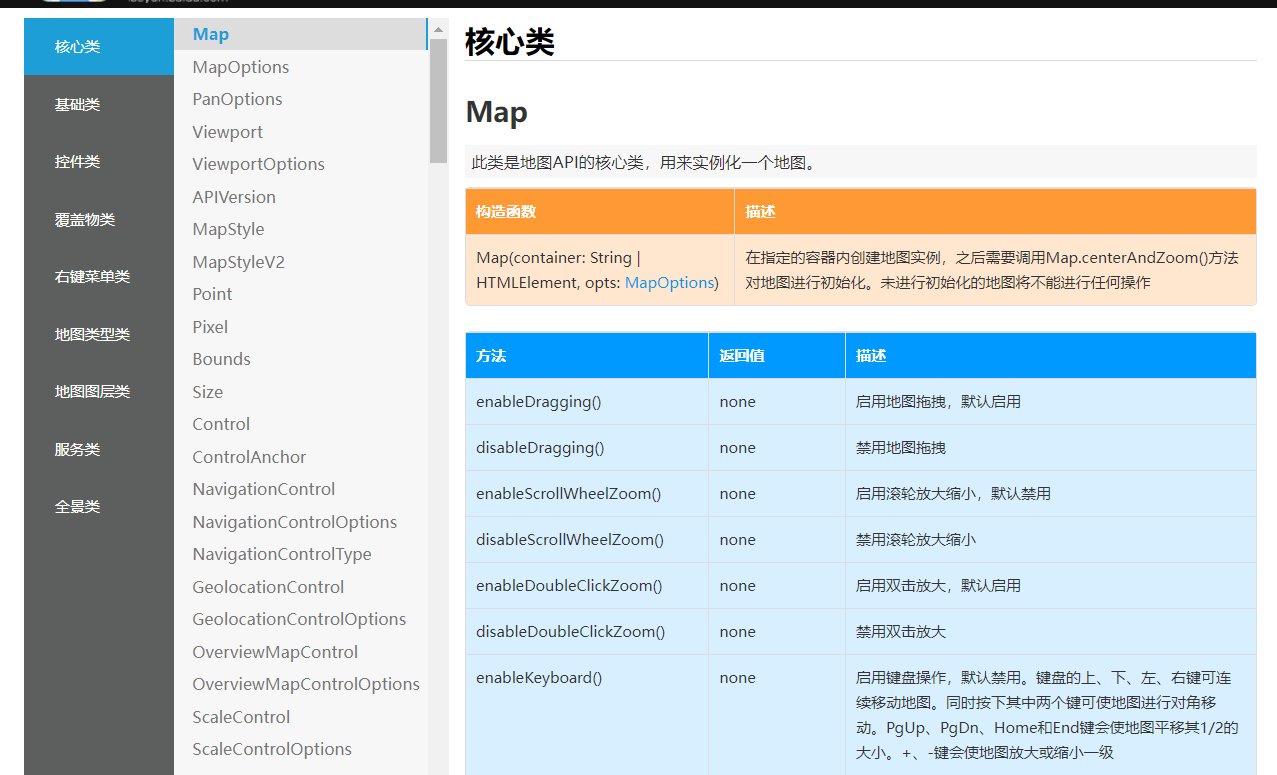
实例化后(第一个参数是容器,第二个是初始配置对象),就可以直接调用
例如禁用拖拽语法:实例对象.disableDragging()




